SNMP
The SNMP driver will communicate with a control device through an SNMP Protocol.
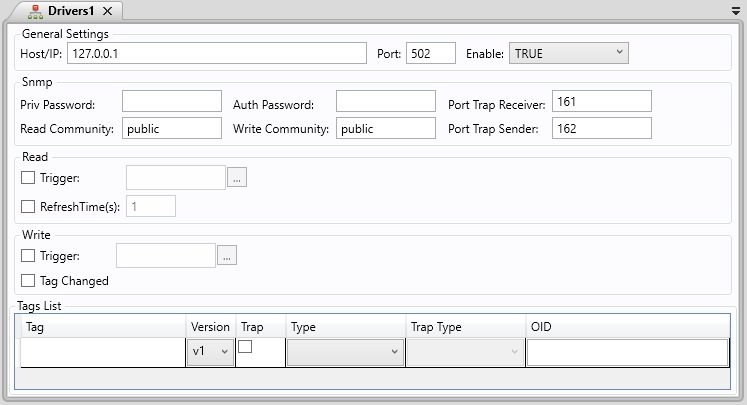
General Settings
. Host/IP: Insert the Host/IP Address of the controller
. Port: Insert the Port of the controller
. Enable: Activates or deactivates the Driver Document
- TRUE: The document will be always activated
- Condition: Activates the document whenever the condition is fulfilled
- FALSE: The document will never activate
SNMP
. Priv Password: Enter the value
. Auth Password: Enter the value
. Port Trap Receiver: Enter the port (default: 161)
. Read Community: Enter the value (default: public)
. Write Community: Enter the value (default: public)
. Port Trap Sender: Enter the value (default: 162)
Read
. Trigger: If checked, will read all the inputs every time a configured tag changes its value. Select the desired tag to use as a Trigger in the TextBox beside it.
. Refresh Time(ms): If checked, will read all the inputs every specified time, in milliseconds.
Write
. Trigger: If checked, will write all the inputs every time a configured tag changes its value. Select the desired tag to use as a Trigger in the TextBox beside it.
. Tag Changed: If checked, will write an input every time its linked tag (of the Tag List) changes.
Tag List
When opening a Driver Document, it will display Driver options in the Ribbon where it is possible to create and delete Driver Items.
A Driver Item is what links a Tag from SmartView to an Input or Output of a Controller.
Once a new Driver Item is inserted, the user will have six fields to configure:
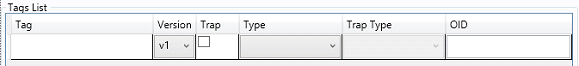
. Tag: Write the Tag that is going to be associated with the specific address
. Version: the Version of a SNMP driver. The versions are V1, V2 and V3
. Trap: Flag if communication will be a trap or not
. Type: Type of object of an SNMP driver. The types are INT, OCTESTRING, OCTESTRINGHEX, OID, IPADDRESS, COUNTER32, GAUGE, TIMETICKS, OPAQUE, COUNTER64 and UNIT.
. TrapType: Type of trap of an SNMP driver if the trap is flagged. The types are:
- ColdStart: A ColdStart trap signifies that the sending protocol entity is restarting itself so that the agent's configuration or the protocol entity implementation can be altered.
- WarmStart: A WarmStart trap signifies that the sending protocol entity is restarting itself so that neither the agent configuration nor the protocol entity implementation can be altered.
- LinkDown: A L inkDown trap signifies that the sending protocol entity recognizes a failure in one of the communication links represented in the agent's configuration.
- LinkUp: A LinkUp trap signifies that the sending protocol entity recognizes that one of the communication links represented in the agent's configuration has come up.
- AuthFail: An AuthenticationFailure trap signifies that the sending protocol entity is the addressee of a protocol message that is not properly authenticated.
. OID: The uniquely identify managed objects in the MIB (MIB stands for Management Information Base and is a collection of definitions that define the properties of the managed object within the device to be managed. MIB files are written in an independent format and the object information they contain is organized hierarchically. The various pieces of information can be accessed by SNMP).
Example:
We configured the communication with SmartView and the OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.2.1.3.0 of SNMP to communicate with read and write as public.
01. Create newtag1, String in the Tags Document.
02. Create SNMP folder in Driver.
03. Create Driver1 document inside SNMP folder.
04. Write 127.0.0.1 in Host/Ip.
05. Write 1611 in Port.
06. Check Refresh Time in Enable Read.
07. Check Tag Changed in Enable Write.
08. Write newtag1 on Tag cell.
09. Select v2 in Version.
10. Select OCTETSTRING in Type.
11. Write 1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.2.1.3.0 in OID.
12. Run the Application.